Best Countries for Digital Nomads in 2026 (Based on Real Constraints, Not Instagram)
Remote work didn’t just “change where we work.” It changed what a life plan looks like. In 2026,

The rise of AI agents—autonomous systems capable of decision-making, learning, and executing tasks—is poised to redefine industries by 2025. Unlike generative AI tools like ChatGPT, which focus on content creation, AI agents act independently, solving complex problems with minimal human input. By 2030, the AI agents market is projected to skyrocket to $47.1 billion, driven by advancements in reasoning, collaboration, and real-world applications. Here’s what businesses and individuals need to know about this transformative technology.
By 2028, Gartner predicts 15% of daily business decisions will be autonomous. Companies without AI strategies risk obsolescence, as competitors like Nvidia already deploy AI agents to accelerate chip design.
3 Steps to Prepare:
Share:
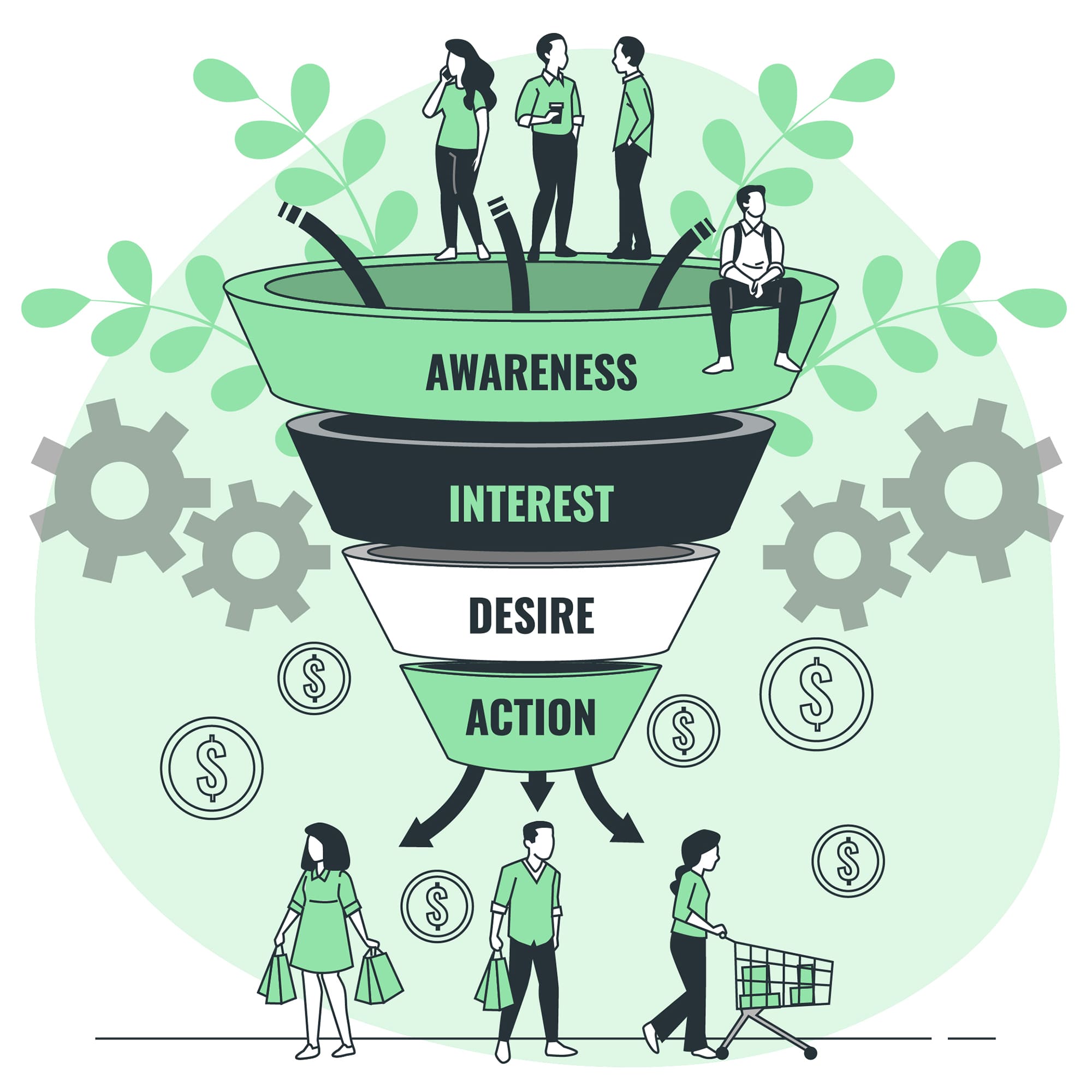
Remote work didn’t just “change where we work.” It changed what a life plan looks like. In 2026,
The 2026 reality: “zero-waste” isn’t a vibe anymore — it’s a workflow A few years ago, zero-waste content
It was 2:30 AM when Sarah finally admitted defeat. Her small jewelry business had a beautiful website, unique
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, adaptability is not just a strength—it’s a necessity. Over the past decade,
Imagine walking into a brick-and-mortar store, spotting a product you like, but struggling to find any helpful information.